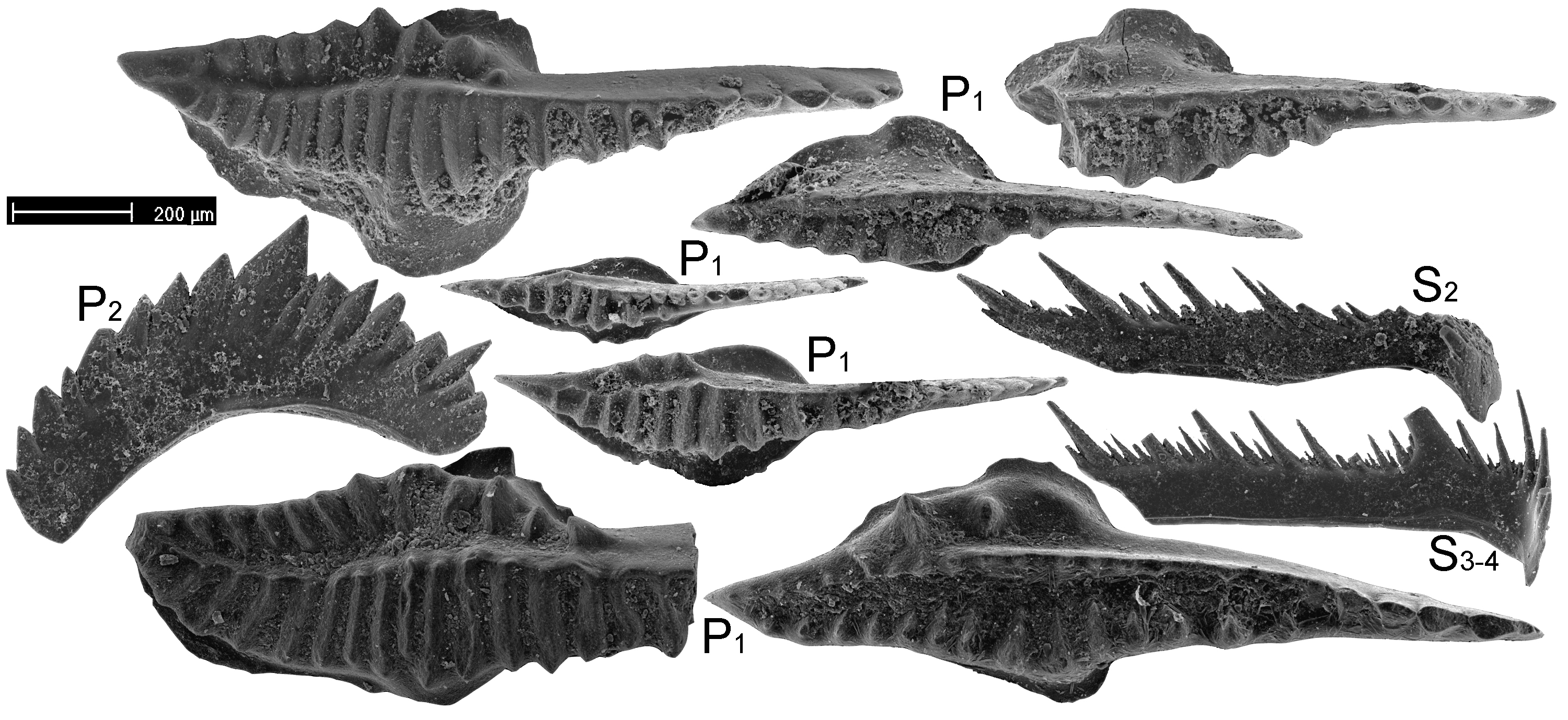
Gromada CONODONTOPHORIDA » Podgromada EUCONODONTA » Rząd Ozarkodinida » Podrząd Ozarkodinina » Rodzina Cavusgnathidae » Rodzaj Pseudopolygnathus »
Pseudopolygnathus ultimus
Sugerowana cytacja: Dzik, J. 2015. Pseudopolygnathus ultimus (Bischoff, 1957) . Ikonoteka (http://ikonoteka.paleo.pan.pl/xwiki/bin/viewrev/Species/Pseudopolygnathus+ultimus+)