Diagnoza
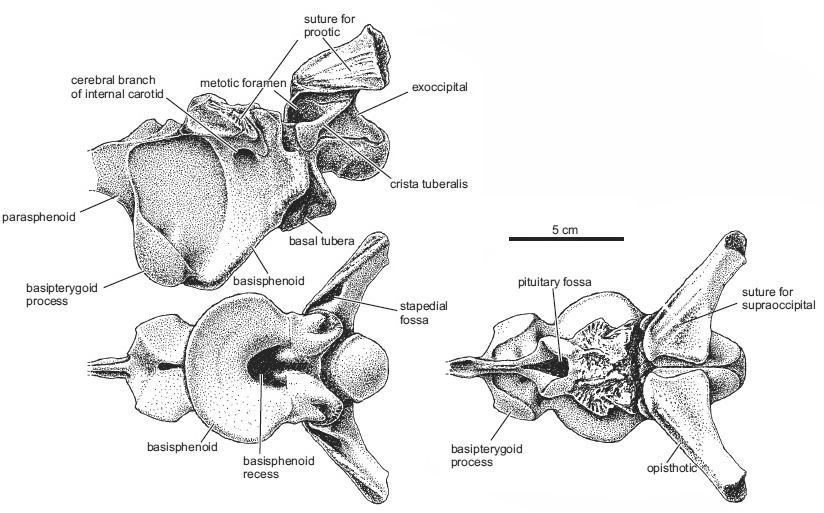
Smok wawelski differs from other carnivorous archosaurs in braincase with funnel−like expansion between the basal tubera and basipterygoid on the ventral surface, which is rounded in outline, much wider than the remainder of the ventral braincase, and indented by a deep pit at its caudal corner.
Porównanie
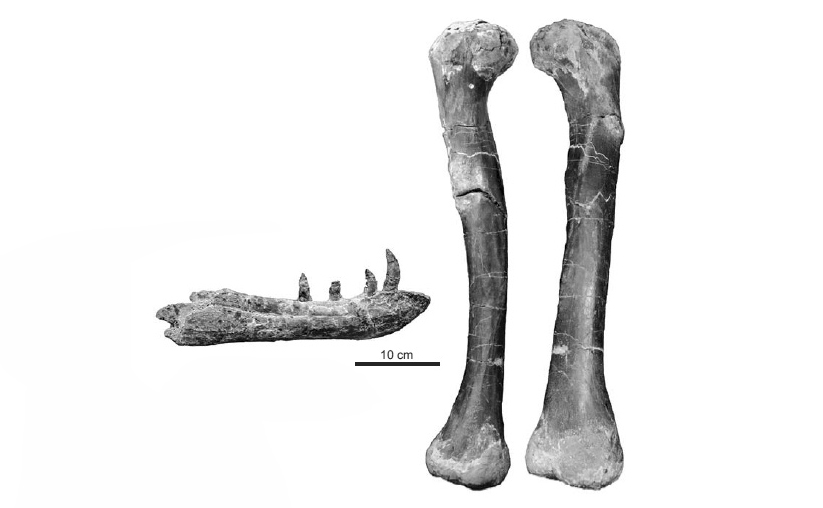
Smok wawelski possesses some features that are common in dinosaurs. These include a supratemporal fossa that extends onto the frontal, three sacral vertebrae, an antitrochanter extending onto the ilium, and an anterior trochanter on the femur. Some features, especially of the braincase, seem reminiscent of larger and more derived theropods, including an increased attachment area for the pterygoideus musculature on the lateral surface of the braincase. However, other features are shared with some crocodile−line archosaurs, especially “rauisuchians” such as Postosuchus and Polonosuchus.
Autekologia
Carnivorous
Występowanie geograficzne
Only locus typicus.
Zasięg czasowy
Only stratum typicum.
Materiały muzealne
Specimens ZPAL V.33/16–56, 97–102, 220, 238, 239, 295–298, 300, 302–304, 306–309, 311–314, 461, 507. (Institute of Paleobiology PAN, Warsaw)
Literatura
Niedźwiedzki, G., Sulej, T., and Dzik, J. 2012. A large predatory archosaur from the Late Triassic of Poland. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 57: 267–276.