Smok wawelski
Sugerowana cytacja: Kapuścińska, A. 2015. Smok wawelski Niedźwiedzki, Sulej & Dzik 2012. Ikonoteka (http://ikonoteka.paleo.pan.pl/xwiki/bin/viewrev/Species/Smok+wawelski)
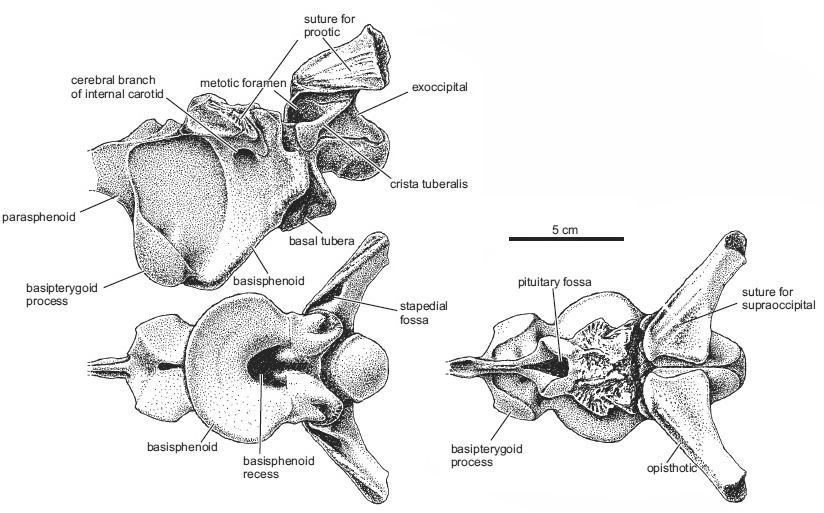
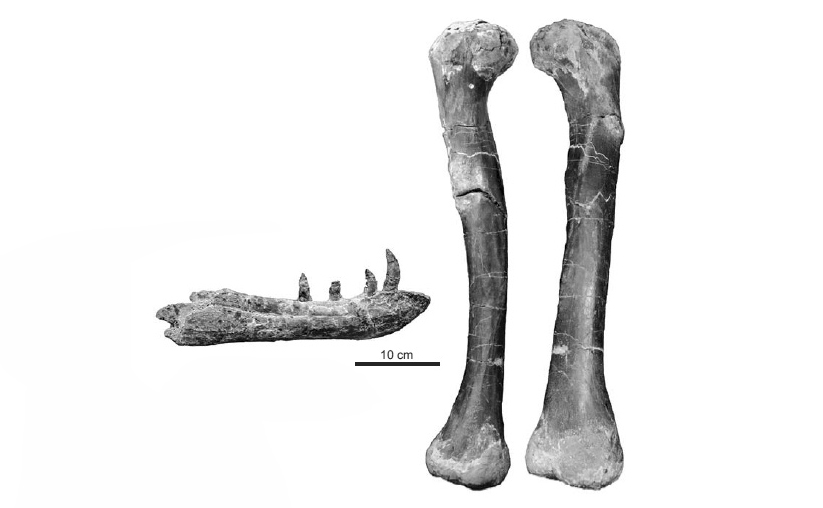
Diagnoza Autapomorphies among archosaurs are designated with an asterisk [*] and the remaining features provide a diagnosis differentiating Smok wawelski from other carnivorous archosaurs (including currently known theropod dinosaurs, “rauisuchians”, crocodylomorphs, ornithosuchids, and phytosaurs). Braincase with funnel−like expansion between the basal tubera and basipterygoid on the ventral surface, which is rounded in outline, much wider than the remainder of the ventral braincase, and indented by a deep pit at its caudal corner*. Nearly entire lateral surface of basisphenoid excavated by a deep fossa for the pterygoideus musculature, such that the midline region between the left and right fossae is extremely thin (< 2 mm)*. Short, sheet−like crista tuberalis (= metotic strut of many authors). Base of the paroccipital process higher than dorsal rim of occipital condyle. Premaxillary body longer than tall, massive, with four large teeth, poorly developed narial fossa, lacking subnarial gap and subnarial foramen between premaxilla and maxilla. Maxilla elongated, with a high body that retains a constant dorsoventral depth as it continues caudally, and with 11 or 12 teeth. Antorbital fenestra low and triangular in outline. Antorbital fossa small, developed only around anterior part of antorbital fenestra. Maxillary and dentary tooth crowns recurved distally, with serrations along both edges and with marginal enamel wrinkles. Postorbital process of jugal curved strongly posteriorly, such that its anterior margin is markedly convex*. Humerus with distinct longitudinal torsion of shaft. Deltopectoral crest less than 30% of length of humeral shaft. Ilium tall (less than 3.5 times longer cranio−caudally than tall above acetabulum), robust with a dorsally extending buttress above the acetabulum, a triangular rugosity on posterior iliac blade, and an antitrochanter, but without a brevis fossa (sensu Novas 1996). Anterior process of ilium elongated such that it reaches past the cranial level of the pubic peduncle. Large, ovoid antitrochanter−like structure on the medial acetabular wall of the ilium, immediately caudal to pubic peduncle*. Sacrum composed of three vertebrae, two are broadly attached to ilia through sacral ribs. The transition from the femoral shaft to the femoral head is interrupted by a notch and shallow depression. Femur with a mound−like lesser trochanter (= anterior trochanter) that is not elevated, a ridge−like fourth trochanter, and no trochanteric shelf. Porównanie Smok wawelski possesses some features that are common in dinosaurs, and have long been regarded as characters unique to dinosaurs (and, in some cases, their closest dinosauromorph relatives). These include a supratemporal fossa that extends onto the frontal, three sacral vertebrae, an antitrochanter extending onto the ilium, and an anterior trochanter on the femur (Bakker and Galton 1974; Gauthier 1986; Sereno 1991, 1999; Langer and Benton 2006; Brusatte et al. 2010a, b; Nesbitt 2011). Some features, especially of the braincase, seem reminiscent of larger and more derived theropods, including an increased attachment area for the pterygoideus musculature on the lateral surface of the braincase (Holliday and Witmer 2008). However, other features are shared with some crocodile−line archosaurs, especially “rauisuchians” such as Postosuchus and Polonosuchus (Chatterjee 1985; Long and Murry 1995; Sulej 2005; Brusatte et al. 2009; Weinbaum 2011). Autekologia Carnivorous Występowanie geograficzne Only locus typicus. Zasięg czasowy Only stratum typicum. Materiały muzealne Specimens ZPAL V.33/16–56, 97–102, 220, 238, 239, 295–298, 300, 302–304, 306–309, 311–314, 461, 507. (Institute of Paleobiology PAN, Warsaw) Literatura |
|